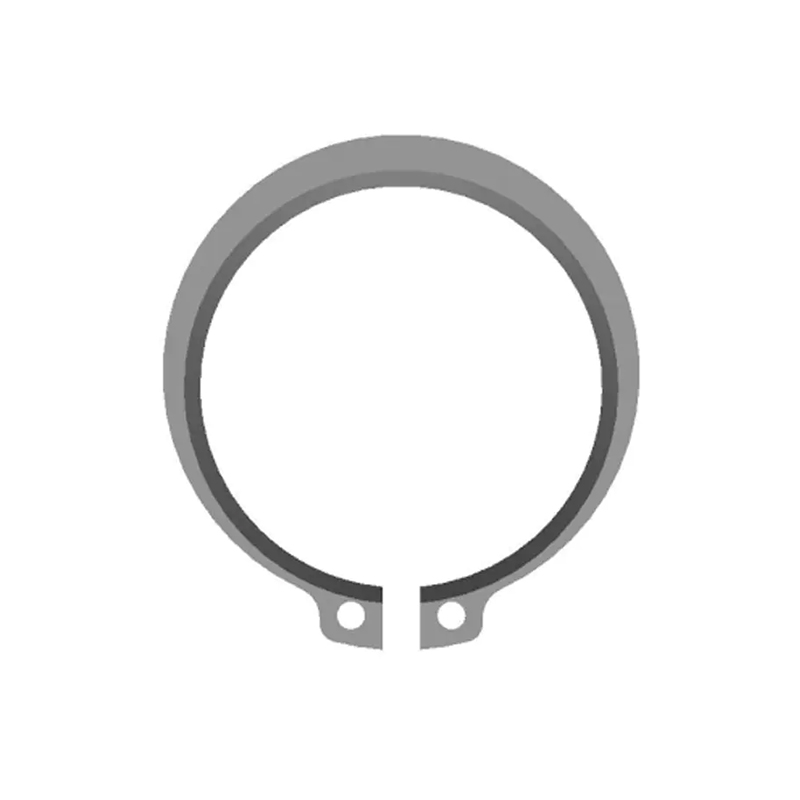
In mechanical engineering and industrial manufacturing, retaining components securely in place is essential for both safety and performance. Among the most widely used retaining solutions is the external circlip. Compact, reliable, and cost-effective, external circlips are critical in applications where rotating parts must be held firmly on shafts while allowing efficient assembly and disassembly. As industries continue to demand high-precision and durable fastening solutions, external circlips remain a cornerstone of mechanical design.
Content
- 1 1. What is an External Circlip?
- 2 2. Key Features and Functions
- 3 3. Types of External Circlips
- 4 4. Materials and Surface Treatments
- 5 5. Applications of External Circlips
- 6 6. Advantages of Using External Circlips
- 7 7. Standards and Quality Control
- 8 8. Innovations and Market Trends
- 9 9. Choosing the Right External Circlip
- 10 Conclusion
1. What is an External Circlip?
An external circlip is a type of retaining ring, usually manufactured from spring steel, stainless steel, or other high-strength alloys. It is designed to fit into a machined groove on the outside of a shaft. Once installed, the circlip exerts radial tension, securely locking components such as bearings, gears, or pulleys in position.
Unlike screws, nuts, or bolts, external circlips provide axial retention without requiring additional hardware. Their simple design, combined with high load-bearing capacity, makes them one of the most efficient shaft-retaining devices available.
2. Key Features and Functions
- Axial Retention: Prevents components from sliding along a shaft while allowing rotation.
- Space Efficiency: Provides strong retention without bulky fasteners.
- Quick Installation: Easily installed and removed with circlip pliers, reducing assembly time.
- High Strength: Made from hardened materials capable of withstanding significant loads.
- Cost-Effectiveness: A low-cost yet highly reliable mechanical solution.
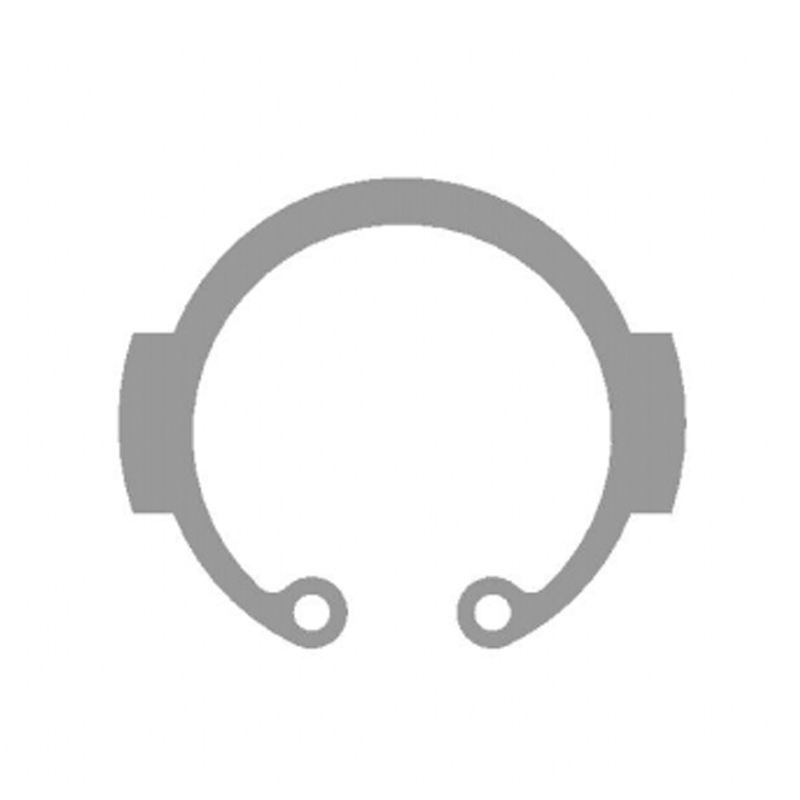

3. Types of External Circlips
Although the basic principle remains the same, external circlips are available in multiple designs to suit different applications:
- Standard External Circlips (DIN 471 / ISO 8752): The most common type, featuring a semi-flexible design for shafts of various diameters.
- Heavy-Duty External Circlips: Thicker and stronger, suitable for high-load environments such as automotive transmissions and heavy machinery.
- E-Clips: A variation of external circlips, designed for easier installation without requiring full shaft access.
- Specialized Circlips: Custom sizes and profiles tailored to specific machinery or performance requirements.
4. Materials and Surface Treatments
The choice of material affects the performance and lifespan of external circlips. Common materials include:
- Carbon Spring Steel: Standard material, offering high elasticity and durability.
- Stainless Steel: Provides corrosion resistance, suitable for marine, chemical, or food-grade environments.
- Beryllium Copper or Phosphor Bronze: Used where non-magnetic or conductive properties are required.
Surface treatments such as phosphate coating, zinc plating, or black oxide finishing improve wear resistance and corrosion protection, extending the service life of the circlip.
5. Applications of External Circlips
5.1 Automotive Industry
External circlips are widely used in automotive transmissions, gearboxes, steering systems, and wheel hubs. They secure bearings and gears on shafts, ensuring reliable performance under high-speed and heavy-load conditions.
5.2 Aerospace and Aviation
In aerospace engineering, external circlips provide critical retention in turbine engines, landing gear mechanisms, and control systems, where precision and durability are essential.
5.3 Industrial Machinery
Heavy-duty equipment such as pumps, compressors, and conveyor systems rely on external circlips to hold rotating parts in place during continuous operation.
5.4 Electrical and Electronics
Small-scale external circlips are used in electric motors, actuators, and precision instruments where compact retention is necessary.
5.5 Marine and Offshore Applications
Stainless steel external circlips are essential in shipbuilding and offshore equipment, where corrosion resistance against saltwater is a priority.
5.6 Consumer Products
From bicycles to household appliances, external circlips play a role in securing moving parts in everyday items.
6. Advantages of Using External Circlips
- Reduced Assembly Cost: Simple design minimizes production and installation costs.
- Reusability: Many circlips can be removed and reused without damage.
- Reliable Performance: Withstands vibration, axial loads, and dynamic stress.
- Versatility: Available in a wide range of sizes and materials for multiple industries.
7. Standards and Quality Control
To ensure consistency and safety, external circlips are manufactured according to international standards such as DIN 471, ISO 8752, and ASME specifications. High-quality control ensures that circlips maintain accurate dimensions, consistent hardness, and reliable performance across demanding environments.
8. Innovations and Market Trends
8.1 Precision Manufacturing
Advances in CNC machining and automated production have improved circlip dimensional accuracy, ensuring tighter tolerances and better performance in high-precision applications.
8.2 Surface Engineering
New coatings such as advanced nitriding, polymer coatings, and eco-friendly plating improve wear resistance and corrosion protection, extending the service life of circlips.
8.3 Lightweight Materials
With the growing demand for weight reduction in automotive and aerospace industries, research into lighter but equally strong materials for circlips is increasing.
8.4 Market Growth
The global market for circlips and retaining rings is expanding, driven by the growth of automotive production, industrial machinery, and consumer electronics. Asia-Pacific leads the market due to its strong manufacturing base, while Europe and North America focus on advanced, high-performance circlips for specialized industries.
9. Choosing the Right External Circlip
Selecting the correct circlip involves several factors:
- Shaft Diameter: Circlips are designed for specific groove diameters.
- Load Requirements: Heavy-duty applications require thicker, stronger circlips.
- Environment: Corrosive environments call for stainless steel or coated variants.
- Installation Method: Consider whether quick assembly (e.g., E-clips) or maximum strength (standard circlips) is needed.
Conclusion
External circlips are indispensable in modern mechanical engineering, providing a simple yet highly effective solution for securing components on shafts. Their combination of reliability, strength, and cost-efficiency makes them a preferred choice across industries such as automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, electronics, and consumer products. As manufacturing technology advances and industries push for higher performance and sustainability, external circlips continue to evolve through better materials, coatings, and precision engineering. Looking forward, they will remain a vital part of both traditional and next-generation mechanical systems.