Content
- 1 Structural Characteristics of a Beveled Retaining Ring
- 2 How the Beveled Design Enhances Load Retention
- 3 Common Applications in Mechanical Assemblies
- 4 Material Selection and Surface Treatments
- 5 Installation Guidelines and Groove Design Considerations
- 6 Performance Advantages Over Standard Retaining Rings
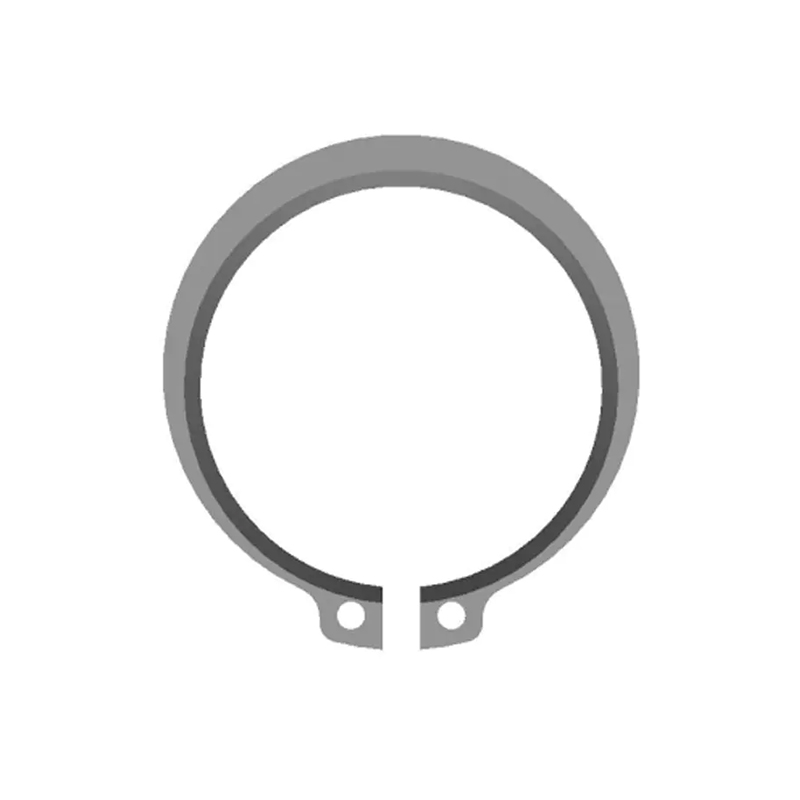
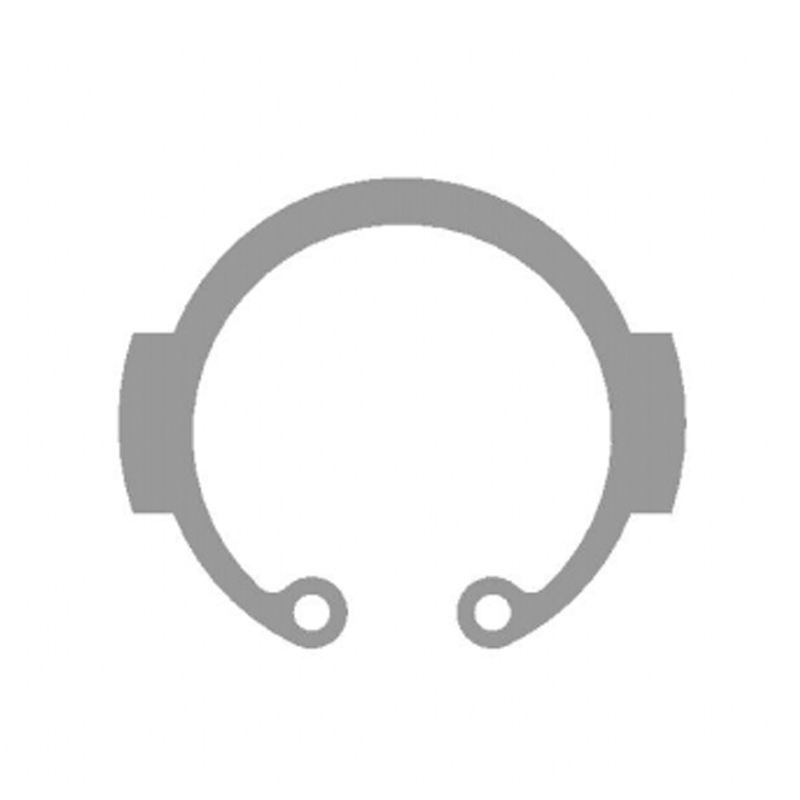
Structural Characteristics of a Beveled Retaining Ring
A beveled retaining ring is a circular fastening component designed with a tapered or angled cross-section that creates a wedging effect when installed into a groove. Unlike standard flat retaining rings, the beveled profile generates axial preload as it seats against the mating component. This preload improves load distribution and reduces axial play in assemblies exposed to vibration or fluctuating forces.
The ring is typically manufactured from spring steel, stainless steel, or carbon steel, and heat-treated to maintain elasticity. When compressed and inserted into a precisely machined groove, it expands outward to secure components such as bearings, gears, pulleys, or bushings on shafts or inside housings.

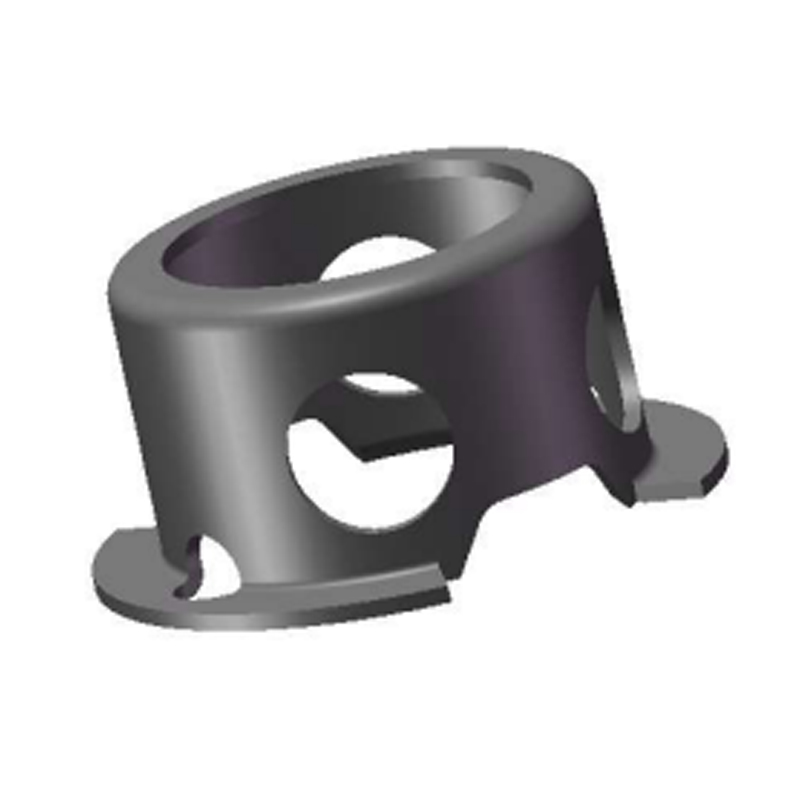
How the Beveled Design Enhances Load Retention
The defining advantage of a beveled retaining ring lies in its angled geometry. Once installed, the tapered edge presses firmly against the retained part, creating consistent axial tension. This mechanical action minimizes endplay and improves resistance to dynamic loads.
- Reduces axial movement in rotating assemblies
- Improves vibration resistance in high-speed machinery
- Enhances load-bearing capability compared to standard rings
- Maintains tighter component positioning under thermal expansion
Because of this preload characteristic, beveled retaining rings are commonly used in applications requiring secure axial retention under continuous operational stress.
Common Applications in Mechanical Assemblies
Beveled retaining rings are widely applied in automotive systems, industrial gearboxes, electric motors, agricultural equipment, and heavy machinery. Their ability to maintain consistent positioning makes them suitable for assemblies where precise axial alignment affects performance and lifespan.
Typical installation scenarios include retaining ball bearings on drive shafts, securing sprockets in power transmission systems, and stabilizing clutch components in mechanical equipment. In electric motors, the ring helps reduce vibration-induced displacement that may otherwise shorten bearing life.
Material Selection and Surface Treatments
Material selection depends on environmental exposure, load requirements, and corrosion resistance needs. Spring steel is often chosen for its high tensile strength and elasticity, while stainless steel provides enhanced resistance in humid or corrosive conditions.
| Material Type | Application Environment |
| Carbon Spring Steel | High-strength industrial machinery |
| Stainless Steel | Moist or corrosive environments |
| Phosphate or Zinc Coated Steel | General-purpose applications requiring surface protection |
Surface treatments such as black oxide, zinc plating, or phosphate coating can improve corrosion resistance and extend service life without altering the ring’s mechanical properties.
Installation Guidelines and Groove Design Considerations
Precision Groove Machining
Accurate groove dimensions are critical for optimal performance. Groove depth, width, and diameter must correspond precisely to the retaining ring specifications. Insufficient groove depth may prevent proper seating, while excessive clearance can reduce preload effectiveness.
Proper Installation Tools
Specialized retaining ring pliers or installation tools should be used to expand or compress the ring evenly. Uneven installation can distort the beveled edge and compromise load distribution. After installation, verifying that the ring is fully seated within the groove ensures consistent axial support.
Performance Advantages Over Standard Retaining Rings
Compared to conventional flat retaining rings, beveled retaining rings provide improved axial retention and reduced component looseness. Their wedging action compensates for minor tolerances and helps maintain structural stability under repetitive mechanical loads.
In high-speed or heavy-duty equipment, this enhanced retention contributes to extended service intervals and reduced maintenance frequency. By maintaining consistent preload and minimizing movement, beveled retaining rings play a key role in ensuring mechanical reliability across diverse industrial applications.