In the intricate world of mechanical assemblies, where components must align perfectly and forces need precise management, one small but critical player often works behind the scenes: the Beveled Retaining Ring. Far more than just a simple fastener, this specialized ring is engineered for reliability, security, and performance in demanding applications. Let's explore why beveled retaining rings are essential precision components.
Content
- 1 What is a Beveled Retaining Ring?
- 2 Why the Bevel Matters: Function & Advantages
- 3 Key Applications: Where Beveled Rings Shine
- 4 Material Choices for Performance & Environment
- 5 Selecting & Installing Beveled Retaining Rings: Best Practices
- 6 Beyond the Basics: Variations
- 7 Conclusion: Precision Where It Counts
What is a Beveled Retaining Ring?
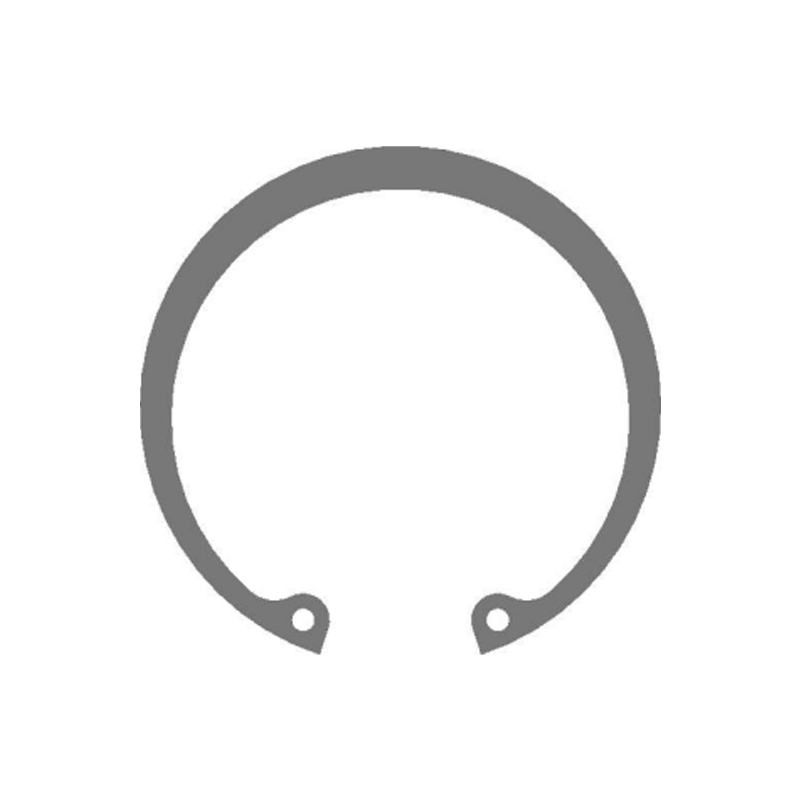
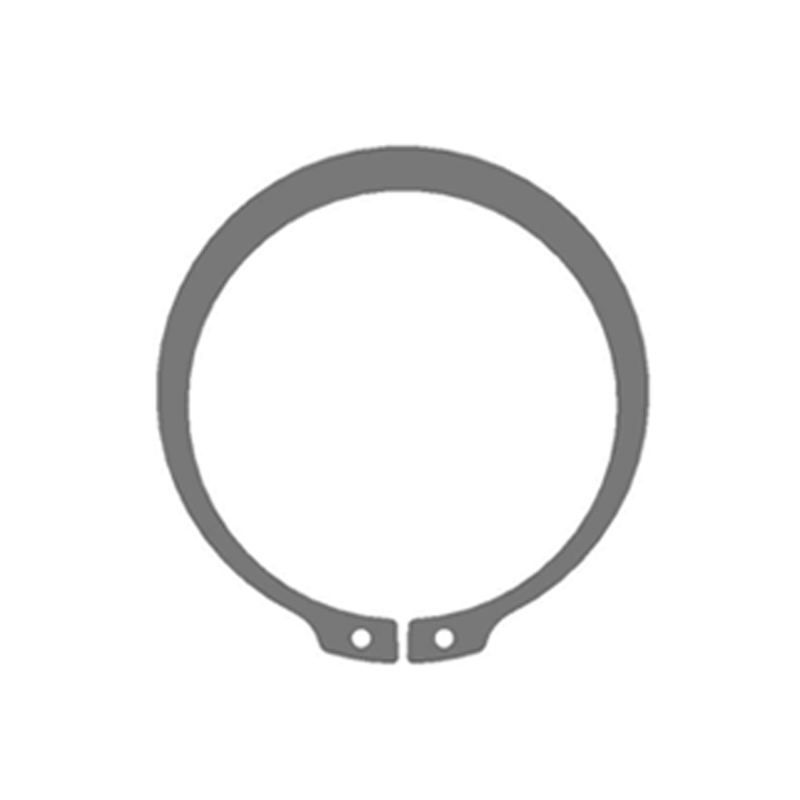
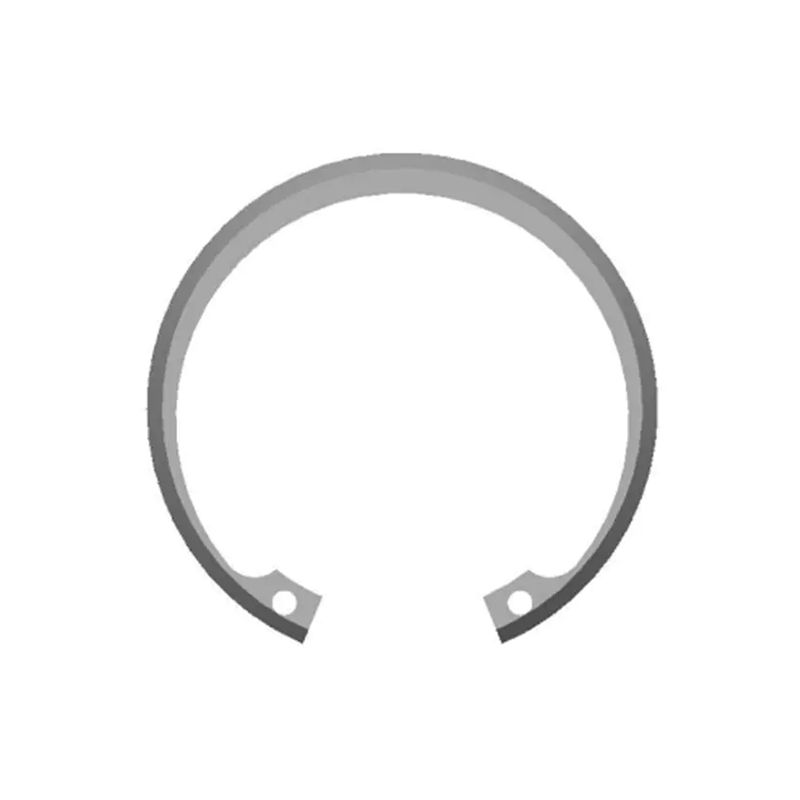
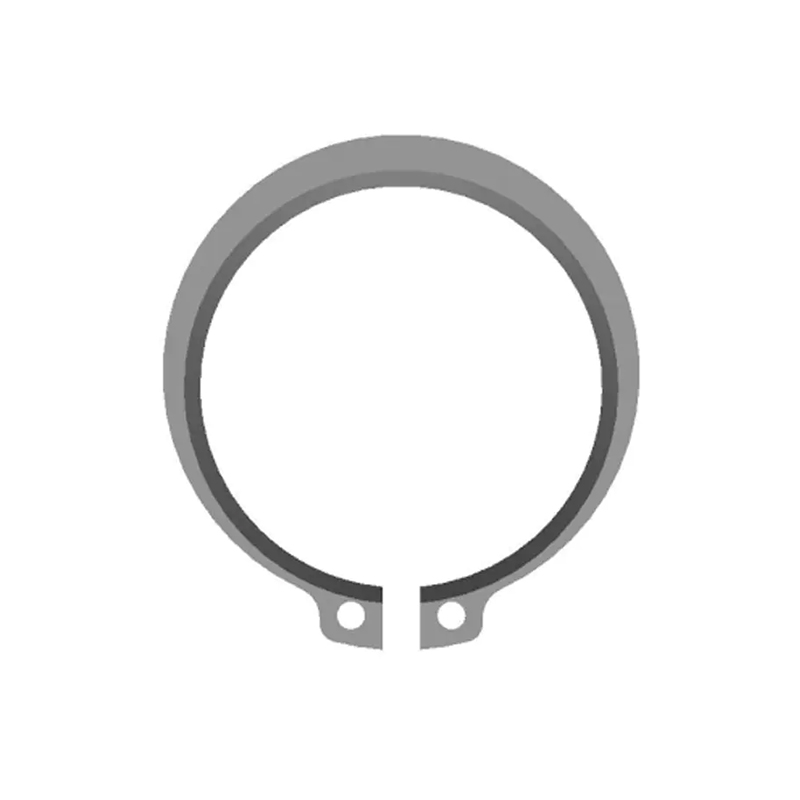
A beveled retaining ring is a type of internal retaining ring designed to fit snugly into a groove on the inside diameter (ID) of a housing or bore. Its defining feature is a precision-ground bevel on its outer edge. This bevel typically angles at 15°, though other angles exist. Unlike standard snap rings, beveled rings are installed using specialized pliers that engage holes in the ring's lugs, allowing for controlled expansion and contraction.
Why the Bevel Matters: Function & Advantages
The bevel isn't just for looks; it's a key functional element providing significant advantages:
-
Controlled Axial Loading: The bevel creates a small contact angle between the ring and the groove wall. This angle allows the ring to handle thrust loads efficiently. The force applied by the component being retained is directed into the groove wall, maximizing load-bearing capacity.
-
Increased Load Capacity: Compared to standard snap rings with a 90° face, the beveled design significantly increases the permissible axial load the ring can withstand. This makes them ideal for high-stress applications like transmissions, pumps, and rotating assemblies.
-
Reduced Stress Concentration: The angled contact helps distribute stress more evenly across the ring and the groove, minimizing the risk of localized deformation or groove damage.
-
Improved Stability & Security: The angled face provides a more positive "lock" against the groove wall, enhancing resistance to vibration and shock loads that could dislodge a standard ring.
-
Precision Fit: Beveled rings are manufactured to tight tolerances, ensuring a consistent and secure fit within the machined groove.

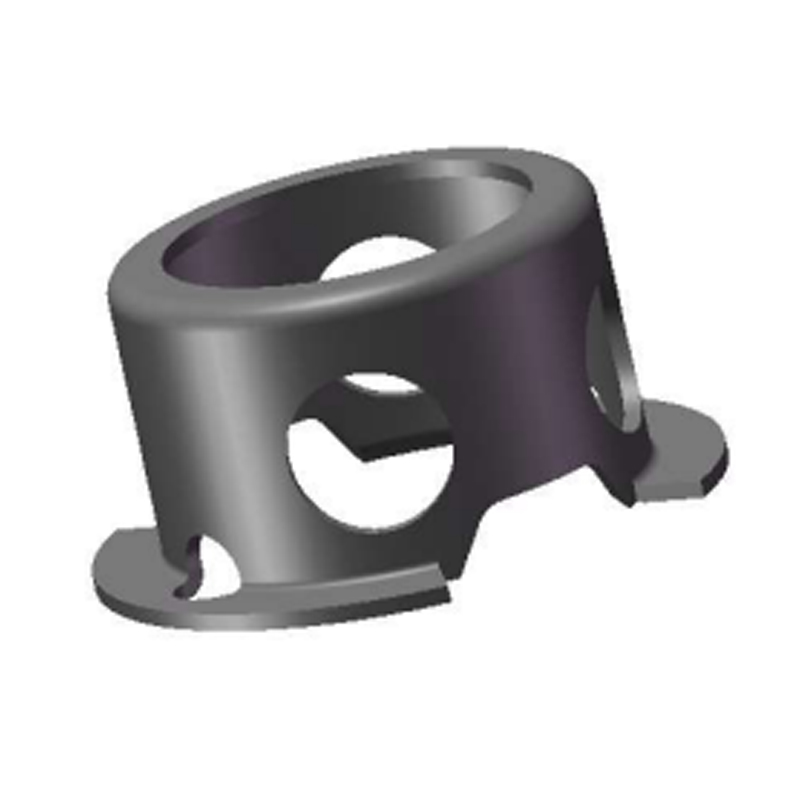
Key Applications: Where Beveled Rings Shine
Beveled retaining rings are the preferred choice in applications demanding high reliability and load-bearing capacity:
-
Automotive & Aerospace: Transmissions, gearboxes, bearing retention in engines and landing gear assemblies.
-
Pumps & Compressors: Securing impellers, bearings, and seals within housings.
-
Power Tools & Industrial Machinery: Retaining gears, bearings, and shafts in motors, gear reducers, and heavy equipment.
-
Medical Devices: Securing precision components in surgical instruments and diagnostic equipment (often using corrosion-resistant materials).
-
Hydraulic & Pneumatic Systems: Retaining pistons, valves, and cylinder components.
Material Choices for Performance & Environment
Beveled rings are available in various materials to suit application requirements:
-
Carbon Steel (CS): Most common, cost-effective, good strength. Often heat-treated (e.g., SAE 1070) and phosphate-coated for corrosion resistance.
-
Stainless Steel (SS): Essential for corrosion resistance (e.g., Type 302/304, Type 316 for marine/chemical environments). Provides good strength.
-
Beryllium Copper (BeCu): Used in explosive environments (non-sparking) and for excellent fatigue strength and conductivity.
-
Inconel (X750): For extreme temperatures and highly corrosive environments.
Selecting & Installing Beveled Retaining Rings: Best Practices
-
Groove is Paramount: The ring's performance depends entirely on a properly machined groove with the correct width, depth, and corner radius (as specified by ring manufacturers). The groove must be perpendicular to the bore axis.
-
Match Ring to Bore: Rings are specified based on the nominal bore diameter they fit into. Ensure the ring size matches the machined bore ID.
-
Installation Tools: Always use the correct internal retaining ring pliers. These pliers have tips designed to engage the ring's installation holes (lugs) without damaging them. Never use screwdrivers or pliers not intended for the purpose.
-
Orientation: Ensure the beveled edge faces the direction of the thrust load it's designed to retain. Installing it backward drastically reduces its load capacity.
-
Inspection: Visually inspect the ring and groove for damage before and after installation. Ensure the ring is fully seated in the groove.
Beyond the Basics: Variations
Standard beveled rings are widely available, but specialized versions exist:
-
Light Duty: For lower load applications where space is limited.
-
Heavy Duty: For maximum load capacity.
-
Inverted Bevel: Less common, for specific load directions.
-
Hooked Lug Rings: Offer increased grip for pliers in hard-to-reach areas.
Conclusion: Precision Where It Counts
The beveled retaining ring exemplifies engineering ingenuity in a compact form. Its angled design transforms a simple concept into a high-performance solution for managing axial loads securely and reliably. When failure is not an option – in high-speed rotations, under heavy thrust, or within critical assemblies – the beveled retaining ring stands as a precision guardian, ensuring components stay exactly where they need to be. For engineers and maintenance professionals, understanding and specifying the correct beveled ring is a crucial step towards robust and dependable machinery.