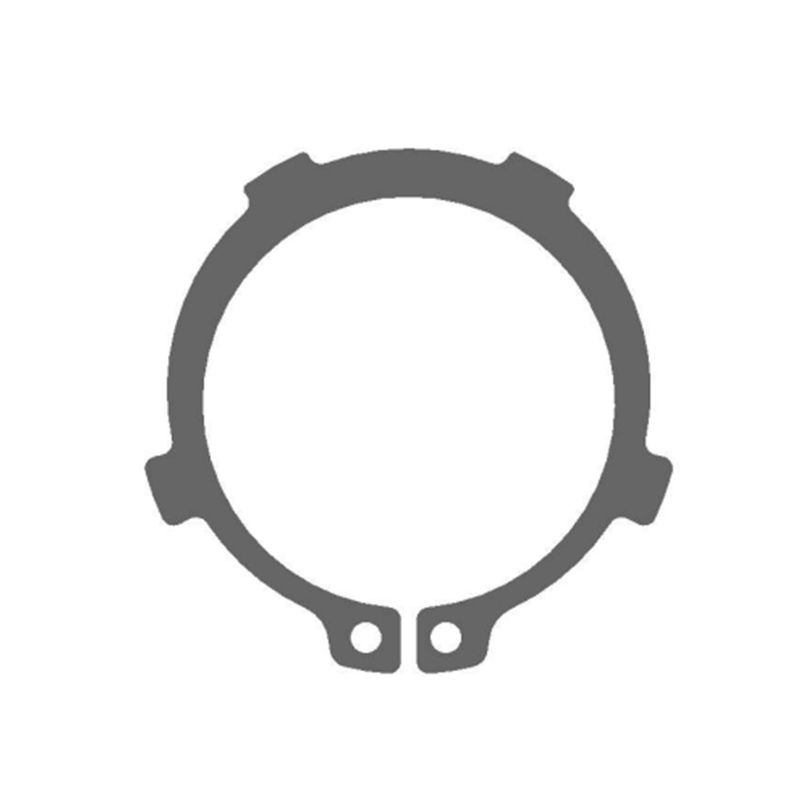
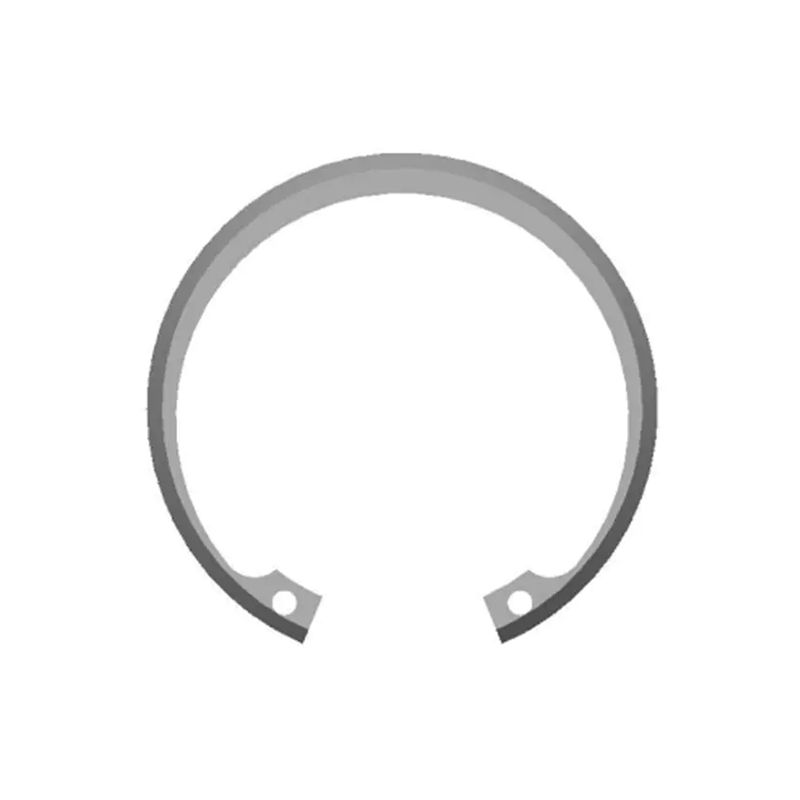
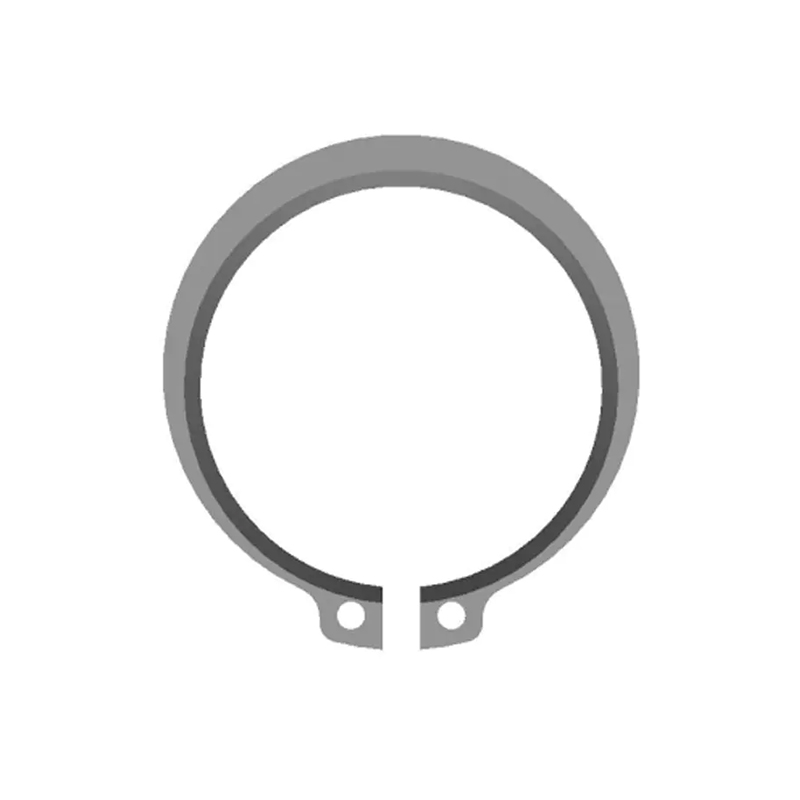
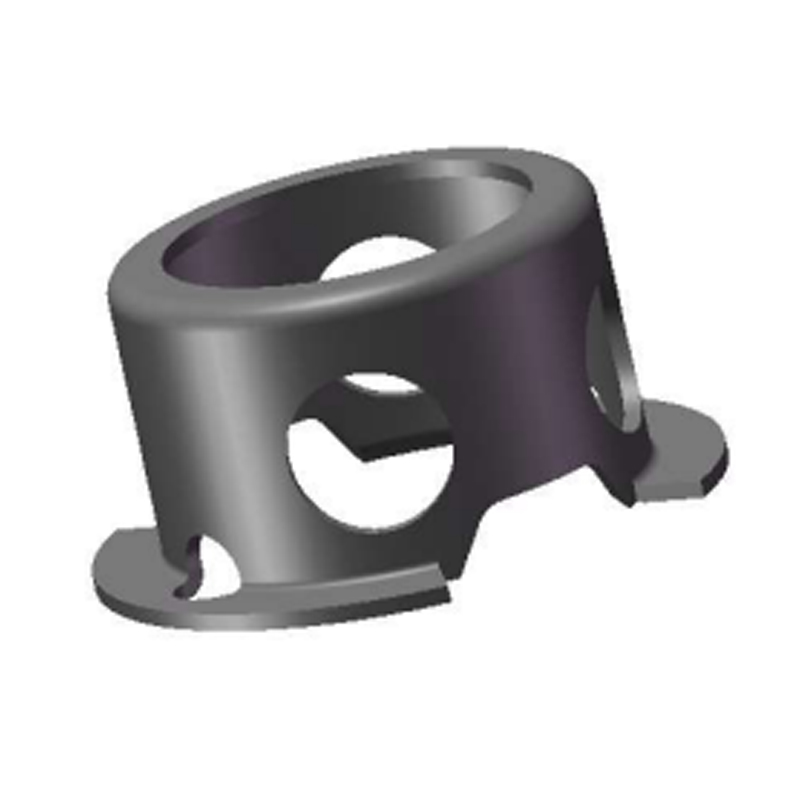
An external snap ring, also referred to as an external retaining ring, is a mechanical fastening component designed to be installed on the outside of a shaft to prevent movement of other components along the shaft’s axis. It fits into a pre-machined groove on the outer diameter of the shaft and serves as a physical stop, preventing attached parts such as bearings, gears, sprockets, pulleys, collars, and washers from sliding off or shifting out of alignment. This function is essential in many mechanical systems where parts are subject to axial forces but must remain properly positioned while allowing free rotation.
Structure and Design
External snap rings are typically made from high-strength spring steel, carbon steel, or stainless steel, providing the necessary elasticity and resistance to deformation. Their design features a semi-open circular shape with two small eyelets or lugs at the ends. These lugs are used with snap ring pliers or retaining ring tools that spread the ring open just enough to slide it over the shaft and snap it into the groove. Once in place, the ring applies an outward radial force that locks it securely in the groove. The exposed edge of the snap ring acts as a shoulder against which other parts can rest.
Use in Mechanical Systems
The most common use of external snap rings is to retain axial positioning of components mounted on a shaft. For example, in gearboxes or power transmission systems, snap rings are used to hold gears or bearings in place so they do not move along the shaft under load. In automotive applications, they are commonly used in transmissions, steering systems, axles, and drive trains to secure rotating parts. Their role is critical in ensuring proper function and preventing failures due to misalignment or excessive movement.
In industrial machinery, such as lathes, conveyor systems, compressors, and pumps, external snap rings maintain the proper spacing and alignment of shafts, bearings, and pulleys. Because they are easy to install and remove, they offer a practical solution for assemblies that may require periodic maintenance or component replacement. Their compact design also saves space, allowing engineers to design systems with tight dimensional constraints without sacrificing performance or durability.
Applications in Different Industries
Automotive Industry: Used extensively in manual and automatic transmissions, wheel hubs, drive shafts, and differential assemblies.
Aerospace and Aviation: Applied in high-precision assemblies where weight and space are critical, such as landing gear and turbine systems.
Electromechanical Devices: Employed in motors, electric drills, and household appliances to secure rotating parts on drive shafts.
Hydraulics and Pneumatics: Retain seals, pistons, and valve elements inside pressurized housings where consistent axial positioning is vital.
Agricultural and Construction Equipment: Found in heavy machinery such as tractors, excavators, and loaders to secure drive components exposed to vibration and heavy loads.
Benefits of Using External Snap Rings
One of the main advantages of using external snap rings is simplicity and efficiency. They eliminate the need for threaded fasteners, flanges, or additional locking mechanisms, which reduces weight and material usage. Installation is quick and requires minimal tools, making them ideal for high-volume production or field repairs. Since they are generally reusable if not damaged, they also contribute to cost savings during equipment servicing or assembly adjustments.
Another benefit is their low profile, which makes them especially suitable in confined mechanical systems. Their holding power is significant considering their compact form, making them both practical and reliable for long-term use under dynamic loads and in high-speed rotating environments.
Maintenance and Considerations
Proper groove design is essential for snap rings to function correctly. The groove must be machined to precise specifications regarding depth, width, and location to ensure that the snap ring seats securely and can withstand the expected forces. In addition, material selection is important depending on the application’s environment. For example, stainless steel snap rings are preferred in corrosive or high-humidity conditions, such as marine or food processing equipment.
It is also important to select the correct snap ring size and type. Standard external snap rings are designed for round shafts, but variations exist for special geometries or loads, including heavy-duty snap rings with thicker cross-sections or beveled edges for added strength.
An external snap ring is a small but crucial mechanical component used to secure parts on a shaft by preventing axial movement. Its widespread use across industries such as automotive, manufacturing, aerospace, and hydraulics is due to its efficient design, ease of installation, cost-effectiveness, and ability to handle dynamic loads in confined spaces. Whether used to hold a bearing in place on a spinning shaft or retain gears in a transmission assembly, external snap rings offer a durable and space-saving solution that supports both mechanical reliability and design flexibility.