Content
Understanding Internal Circlips for Bore Retention
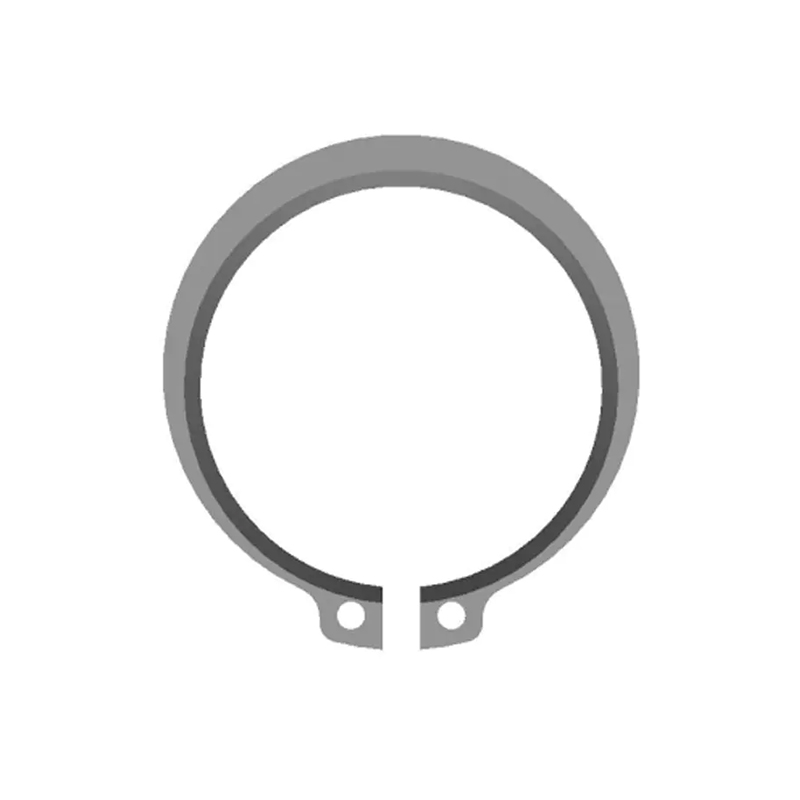
Internal circlips, also known as internal snap rings or retaining rings, are essential components for securing assemblies inside a bore. They are installed in machined grooves within cylindrical bores to retain bearings, gears, or other components, preventing axial movement. Their compact design allows for efficient use of space, making them ideal for automotive, industrial, and mechanical applications where precise axial retention is required.

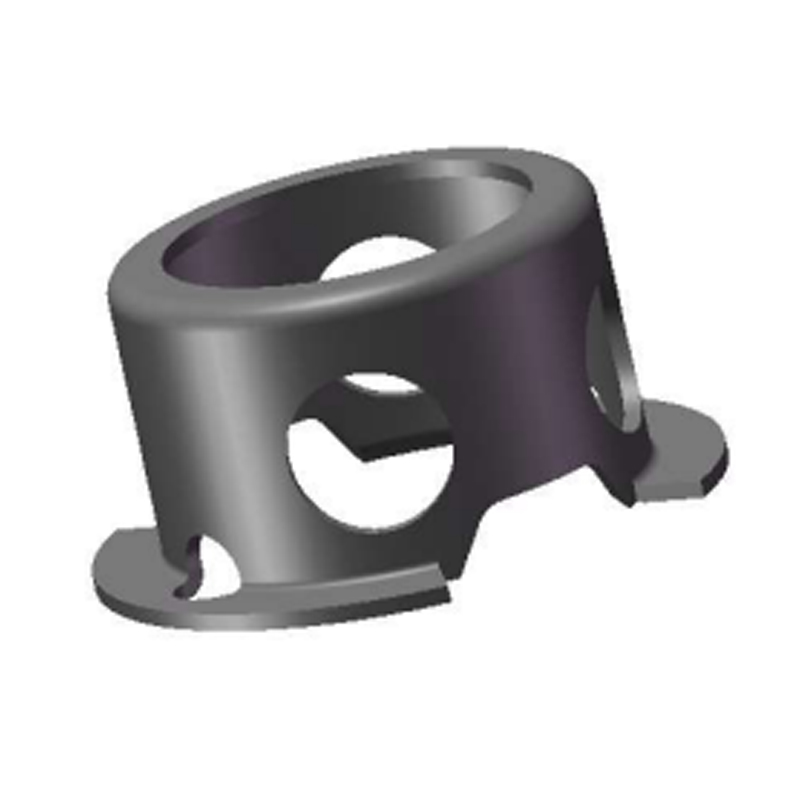
Applications of Internal Circlips
Internal circlips are widely used in mechanical and industrial systems to provide reliable axial retention within bores. Common applications include securing ball bearings, roller bearings, and bushings, as well as retaining gears and pulleys within housings. Their versatility allows them to function in both low-speed assemblies and high-performance equipment operating under dynamic loads.
Automotive Applications
In automotive assemblies, internal circlips are commonly used in transmissions, differential housings, and engine components. They maintain precise positioning of bearings and gears, which is critical for smooth operation and longevity. The ability to withstand axial forces and vibration ensures the integrity of moving parts over extended service intervals.
Industrial and Machinery Applications
Industrial machinery often relies on internal circlips for axial retention in pumps, motors, and gearboxes. In these environments, circlips must endure repetitive motion, high-speed rotation, and varying temperatures while retaining components accurately. Proper selection ensures consistent machine performance and reduces the risk of downtime due to component displacement.
Material Options and Surface Treatments
Internal circlips are manufactured from various materials, each selected to match the operating environment and load requirements. Spring steel is the most common, offering excellent resilience and fatigue resistance. Stainless steel is used for corrosion resistance in humid or chemically aggressive environments. Surface treatments such as phosphate coating or passivation can further enhance corrosion resistance and reduce friction during installation.
Comparing Material Properties
| Material | Key Property | Typical Application |
| Spring Steel | High resilience, fatigue resistance | General mechanical assemblies |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistance | Marine, chemical, or humid environments |
| Phosphate Coated Steel | Improved wear resistance and friction reduction | High-frequency installation and maintenance environments |
Sizing and Selection Considerations
Selecting the correct internal circlip requires careful evaluation of bore diameter, groove width, axial load, and component tolerances. Standardized specifications such as DIN 472 or ISO 13337 provide guidance on dimensions, tolerances, and material performance. Choosing an appropriately sized circlip ensures proper retention without causing deformation of the bore or excessive stress on the circlip itself.
Key Selection Factors
- Bore diameter and groove dimensions to match component tolerances.
- Axial load capacity to withstand operational forces.
- Material and surface treatment based on environmental conditions.
- Ease of installation and removal with suitable tools.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Proper installation is critical to ensure that internal circlips function correctly. Using specialized circlip pliers reduces the risk of bending or deforming the ring during insertion or removal. Regular inspection of wear, deformation, and corrosion ensures long-term performance, particularly in high-speed or high-load applications.
- Use pliers designed for internal circlip installation and removal.
- Inspect grooves for wear or deformation before assembly.
- Replace circlips showing fatigue, corrosion, or cracking.
- Ensure proper seating within the groove to prevent axial displacement.
Conclusion: Optimizing Bore Retention with Internal Circlips
Internal circlips provide an efficient, space-saving solution for axial retention in bores across automotive, industrial, and machinery applications. Understanding their applications, material options, sizing requirements, and installation best practices ensures reliable performance, component longevity, and operational safety. By selecting the right internal circlip for each assembly, engineers can achieve precise retention while maintaining the efficiency and durability of mechanical systems.