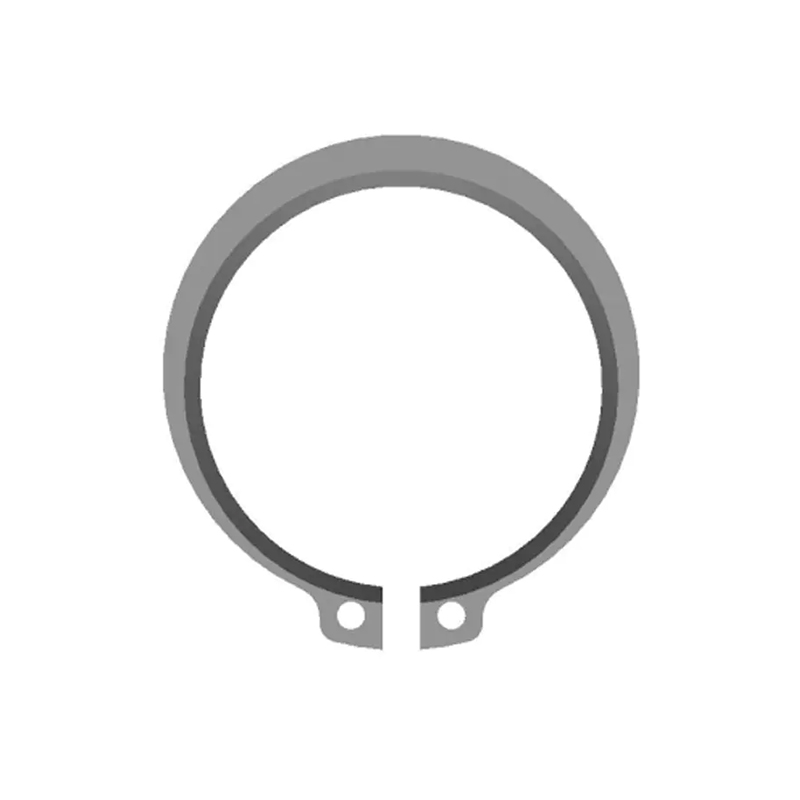
Retaining rings and snap rings are essential components in mechanical assemblies, providing axial positioning for shafts, housings, and other parts. Although these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they have distinct designs, installation methods, and applications. Understanding their differences is critical for engineers, designers, and maintenance professionals to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Content
What Are Retaining Rings?
Retaining rings, also known as circlips or retention rings, are mechanical fasteners that fit into grooves on a shaft or inside a bore. They provide a secure shoulder to locate or lock components in place. Retaining rings are widely used in automotive, industrial, aerospace, and consumer products.
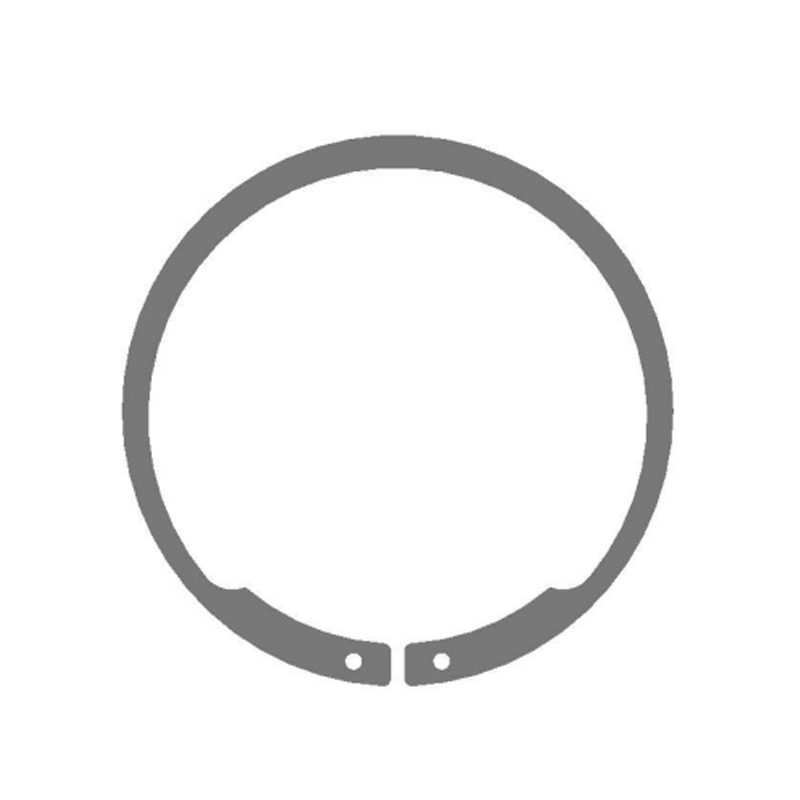

Types of Retaining Rings
- External Retaining Rings: Installed on the outside of a shaft to prevent lateral movement of components along the shaft.
- Internal Retaining Rings: Installed inside a bore or housing to secure components within a cylindrical cavity.
- Spiral Retaining Rings: Continuous rings that offer 360-degree contact with the groove, providing higher load capacity and vibration resistance.
- Tapered Section Retaining Rings: Designed for high-precision applications with tapered grooves for tight fit and minimal axial play.
What Are Snap Rings?
Snap rings are a specific type of retaining ring, often characterized by open ends that can be expanded or contracted during installation. Snap rings are usually manufactured in spring steel and can be installed using pliers or special tools. They are commonly used in automotive gear assemblies, bearings, and machinery components.
Types of Snap Rings
- External Snap Rings: Fit over a shaft and hold components in place with radial pressure.
- Internal Snap Rings: Fit inside a bore to prevent axial movement of internal components.
- Heavy-Duty Snap Rings: Designed for high-load applications with thicker cross-sections for increased strength.
Key Differences Between Retaining Rings and Snap Rings
While retaining rings and snap rings share the purpose of securing components, there are several important differences:
| Feature | Retaining Ring | Snap Ring |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Continuous or solid ring, may have open ends | Usually has open ends for expansion/contraction |
| Installation | Can be snapped into grooves manually or with tools | Requires pliers or special installation tools |
| Load Capacity | Moderate to high depending on design | Generally moderate, suitable for light to medium loads |
| Applications | Industrial machinery, automotive, aerospace, consumer products | Bearings, gears, shafts, automotive assemblies |
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Proper installation and maintenance are critical for the performance of retaining and snap rings. Consider the following points:
- Always ensure the groove dimensions match the ring specifications to prevent movement or failure.
- Use the correct installation tool to avoid deformation or damage to the ring.
- Regularly inspect rings for wear, corrosion, or deformation, especially in high-load or high-vibration environments.
- Replace rings during maintenance cycles to prevent accidental component dislodgement.
Choosing the Right Type for Your Application
Selecting between a retaining ring and a snap ring depends on the application requirements:
- For applications requiring high load capacity or 360-degree contact, spiral or solid retaining rings are preferred.
- For ease of installation and moderate load applications, snap rings are suitable.
- Consider environmental factors such as corrosion, temperature, and vibration when choosing material and coating.
- Internal vs. external selection is determined by whether the component is within a bore or on a shaft.
Conclusion
Retaining rings and snap rings are crucial for maintaining the integrity of mechanical assemblies. Understanding their differences in design, installation, load capacity, and applications allows engineers to choose the right component for each scenario. By selecting the proper ring type and following installation best practices, mechanical systems achieve higher reliability, safety, and performance.